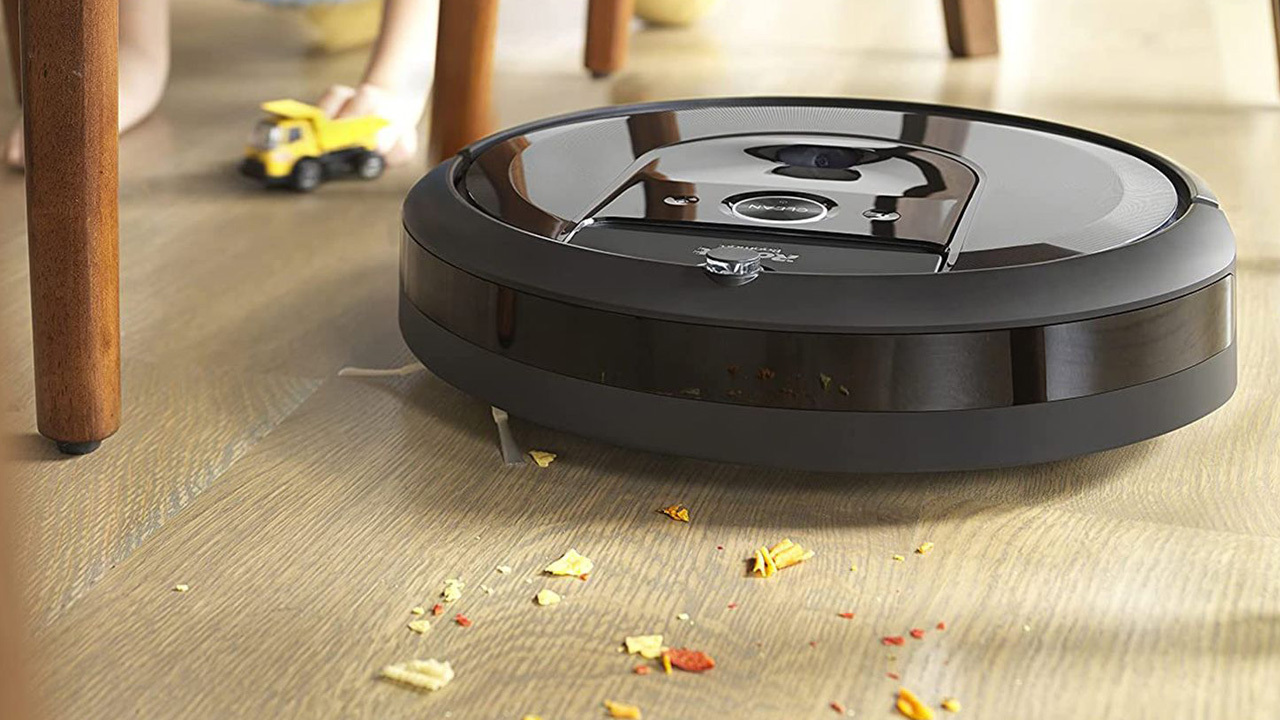
iRobot, the company best known for the Roomba robotic vacuum, has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the United States as it prepares to be acquired by its primary manufacturing partner, Picea Robotics. The move marks a sharp reversal for a business that once defined the consumer robot vacuum category and was valued in the billions just a few years ago.
The bankruptcy filing, submitted in Delaware, follows months of financial strain. iRobot had already warned earlier this year that its ability to continue operating was in doubt. While the company remains a recognizable name in markets such as the United States and Japan, it has struggled to defend its position against lower-priced competitors, particularly Chinese manufacturers offering similar features at aggressive price points. That pressure has forced repeated price cuts and higher spending on product development, steadily narrowing margins.
In 2024, iRobot generated roughly $682 million in revenue, but profitability continued to deteriorate. Competition from companies such as Ecovacs Robotics has reshaped the robot vacuum cleaner market into one where scale manufacturing and cost control matter as much as brand recognition. iRobot’s reliance on overseas manufacturing has further complicated matters, especially as U.S. trade policy shifted. New tariffs, including a 46% levy on imports from Vietnam where many of iRobot’s products for the U.S. market are assembled, added an estimated $23 million in costs in 2025 alone, according to court filings.
The company’s balance sheet was already strained by debt tied to a 2023 loan, taken out while regulators in Europe reviewed a proposed $1.4 billion acquisition by Amazon. That deal ultimately collapsed, leaving iRobot without a buyer and still responsible for approximately $190 million in obligations. After iRobot fell behind on payments, Picea Robotics acquired the debt from funds managed by the Carlyle Group, positioning itself as the company’s primary creditor.
Under the restructuring plan, Picea will assume full ownership of iRobot, cancel the remaining loan balance, and forgive an additional $74 million owed under existing manufacturing agreements. Other creditors and suppliers are expected to be paid in full. iRobot has stated that the bankruptcy process should not interrupt customer-facing services, including app functionality, product support, or supply chain operations.
Founded in 1990 by three MIT roboticists, iRobot originally worked on defense and space robotics before launching the Roomba in 2002. The product helped popularize autonomous household cleaning and drove strong growth for nearly two decades. At its peak in 2021, amid pandemic-driven demand, the company was valued at about $3.56 billion. Today, its market value has fallen to roughly $140 million.
Despite its financial collapse, iRobot still holds an estimated 42% share of the U.S. robot vacuum market and about 65% in Japan. Whether those positions can be maintained under private ownership will depend on how effectively the company adapts to a market that has become more crowded, price-sensitive, and less forgiving of operational missteps.