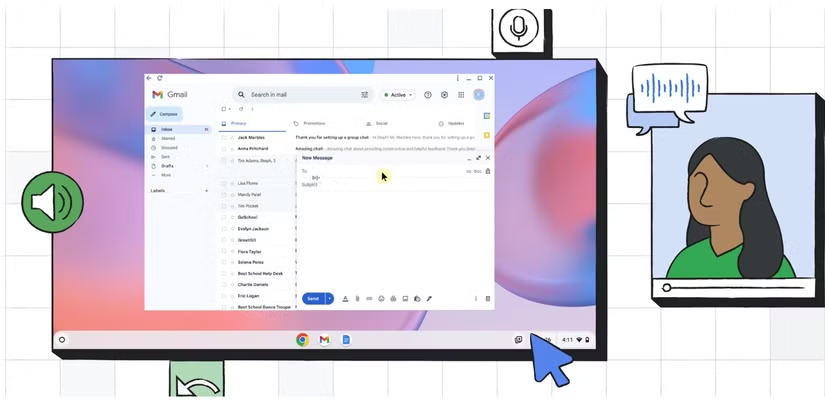
Google has quietly introduced a hands-free control feature for Chromebooks that lets users navigate their device using facial movements—no mouse or touchpad required. Tucked into the Accessibility settings under the latest ChromeOS version (M132 or later), Face Control uses a combination of machine learning and your device’s webcam to translate subtle facial gestures into cursor movements and commands.
Face Control relies on a 478-point 3D mesh mapped from the user’s face using the built-in webcam. This real-time mesh allows the system to detect nuanced movements—such as nods, head tilts, or shifts in expression—and convert them into on-screen actions like clicking, scrolling, or moving the cursor. For users with mobility impairments, it’s a potentially transformative tool. But it also opens up new possibilities for general hands-free computing, whether you’re multitasking, working in limited space, or just trying out something new.
To use Face Control, your Chromebook must be updated to ChromeOS M132 or newer. First-time users will need to download a small machine learning model to enable the feature. Google recommends using the tool in a well-lit environment with the webcam unobstructed for best performance.
You can activate Face Control by opening the Settings app, selecting Accessibility from the left-hand menu, and then navigating to Cursor and touchpad. There, you’ll find the Face Control toggle. Once enabled, you’ll be able to configure various gesture-based commands and customize how your facial movements interact with the cursor.
Google has also included a number of adjustable settings, allowing users to fine-tune how sensitive the system is to movement and what each type of facial gesture does. These customization options make Face Control accessible and functional for a wider range of users and use cases.
The feature is part of a broader trend in accessibility innovation being embraced across tech platforms. Like Apple’s double-tap control for the Apple Watch, Google’s Face Control might start as an accessibility feature—but its usefulness could extend far beyond that.